TERPENES/TERPENOIDS (TUR-peen) -diverse group of organic HydroCarbons (C5H8), produced by a wide variety of plants -terpenoids are.
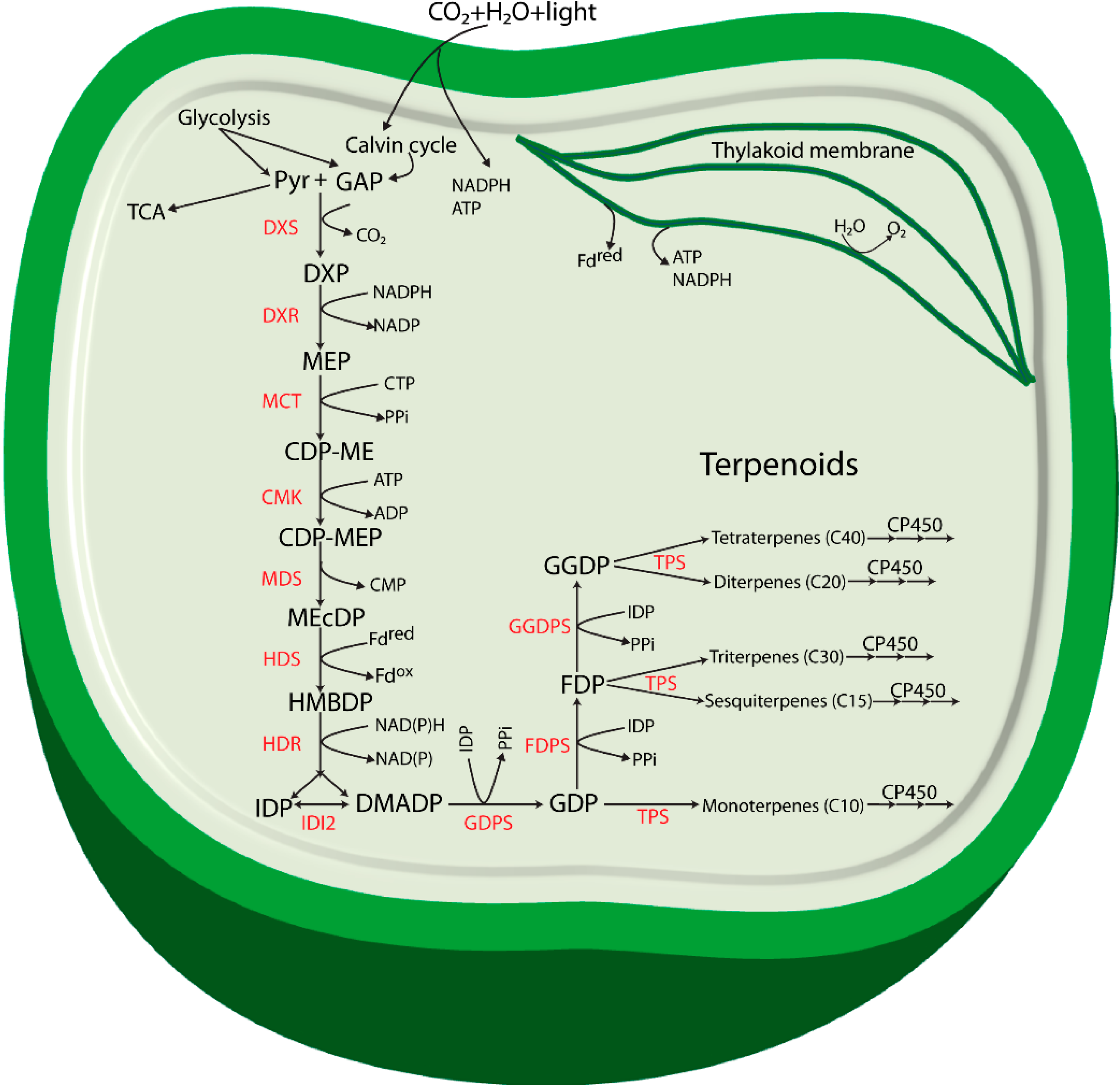
The terpenoids, sometimes called isoprenoids, are a large and diverse class of naturally-occurring organic chemicals similar to terpenes, derived from five-carbon isoprene units assembled and modified in thousands of ways. Terpenes are hydrocarbons resulting from the combination of several isoprene units. Terpenoids can be thought of as modified terpenes, wherein methyl groups have been moved or removed, or oxygen atoms added. Terpene biosynthesis Terpenoids are vital for life of most organisms in exerting metabolic control and in mediating intra- and inter-species interactions, for example, pollination and defense in plants. In plant terpenoid biosynthesis two different pathways synthesize the main building block, isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) (fig. 1); the methylerythritolphosphate (MEP) pathway (also named 1-deoxy-D-xylulose (DOX) pathway) in the chloroplast forms IPP for mono- and diterpenoids, and the mevalonic acid (MVA) pathway in the cytosol, produces IPP for sesquiterpenoids.

Raid Air Game Instructions English. TERPENES/TERPENOIDS (TUR-peen) -diverse group of organic HydroCarbons (C5H8), produced by a wide variety of plants -terpenoids are terpenes which have been chemically. The Salkowski test can be used to identify the presence of terpenoids. Meroterpenes are any compound, including many natural products.
A method of medical treatment for a medical condition in a mammal, said condition being selected from the group consisting of viral infections, bacterial infections, fungal infections, dermatoses, indolent neoplasms, sunburn, burns and swollen joints, said method comprising the parenteral application to said mammal of a pharmacologically effective amount for treatment of said condition of an ozonide of a termpene in a pharmacologically acceptable carrier or excipient.